Search Queries Report
The Search Queries report allows you to monitor the keywords queried by readers. Open the Projects page and click Portal → Reports in the left-hand navigation panel to examine this report. The Report Center page will open. Next, click Reader Behavior → Search Queries in the left-hand navigation panel. And you'll see a chart.
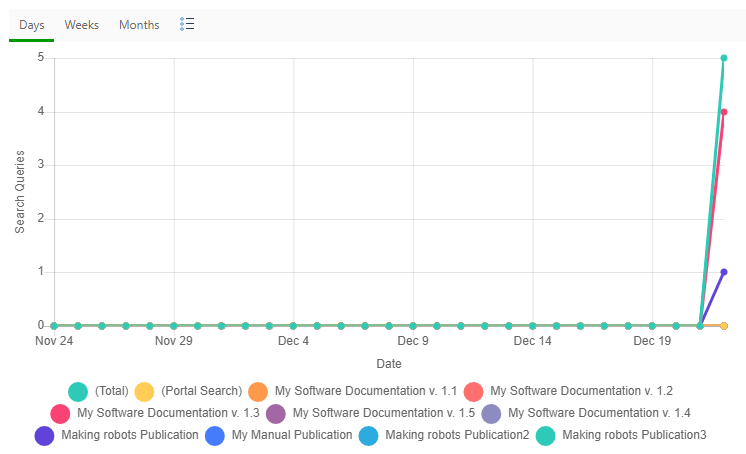
- Total. The total number of search queries both in Portal Search and Publications.
- Portal Search. The global portal search queries. This happens when a reader uses the search box on the portal Home page or the No Filter mode on the portal Search page.
- Publication. The number of search queries in a particular Publication. This happens when a reader uses the search box in the top-right corner of the topic reading page. This box defaults to searching in the current publication only, also giving the Search entire portal option that opens the portal Search page.
There is a table with data under the chart.
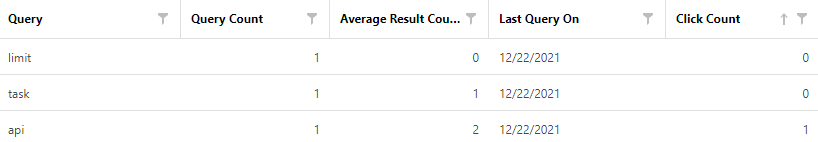
- Query. The search query.
- Query Count. The number of searches for that specific query.
-
Average Result Count. The arithmetic mean of the number of search results shown for all these queries.
Note The number of results can differ when users with different access levels search for the specified query. For example, some users may not have access to a publication containing the query results. - Last Query On. The date when this query was made last.
- Click Count. The number of search result clicks users made in the search results of a query.
For more precise and actionable analytics, reader behavior events (search queries, topic views) are not tracked for web crawlers and logged in contributors, those events are only tracked for anonymous readers and logged in Power Readers.
How to interpret these statistics? Here are some use cases:
- The Click Count for the Task query is zero. It means that the found content isn't relevant to the search of readers, as they think. So, you should consider adding a topic that answers that query or changing the title of an existing topic so readers perceive it as a relevant topic to read.
- As you see, the Average Result Count for the Limit query is zero. It means that readers use this keyword for searching, but there is no such topic in your documentation. Consider creating a topic that answers that query. On the contrary, the Average Result Count for the API query is two. It means that there are two topics shown in search results for that very query.
- Last Query. Let's assume you rename a term in the product you document. The Last Query of the term was a year ago, for example. So you should ignore this query in your analysis; people don't search for it anymore. You can hide it by using filters.
The Full-Text Search engine indexes three sources of content:
- topic content;
- topic title;
- topic Index Keywords.
Using Index Keywords is an excellent way to improve your search results when some term is not directly mentioned in a topic, but that topic is highly relevant to that term. Readers may find a topic by searching for a term used in the Index Keywords.
All the screenshots above represent the Entire Portal view of data. You can see the same reports for a specific project — select it in the Report for dropdown box in the report header panel. Moreover, you can group, sort, and filter the results. Learn more on this here: Working with Data Tables.