Information Products: Definition, Types, Examples
 Elmirain Technical Writing on 11/23/2022 — 7 minute read
Elmirain Technical Writing on 11/23/2022 — 7 minute read Elmirain Technical Writing on 11/23/2022 — 7 minute read
Elmirain Technical Writing on 11/23/2022 — 7 minute read

Today, we live, communicate, and learn in an information space. Moreover, we trade in this space, and it is now normal to speak of knowledge monetization and information products. In the long run, the latter may materialize, for example, become real books sold in hard copies – this may happen when your information product becomes so popular that everyone wants to have a copy on the bookshelf as a symbol of being related to it.
This happens to outstanding information products like, for instance, Dale Carnegie’s bestseller “How to make friends and influence people.” You can easily access it online and read it free in fb2, pdf, or any other format. But many readers want a hard copy and keep it as a souvenir like we keep printed photos. It may be a reference to some period in the owner’s life or just a wish to have a hard copy in a home collection of psychology books.
Successful information products usually travel a long way to a hard copy version, but this is preceded by a period online when the product is developed, brought to the market, positioned, advertised, sold, reviewed, edited, republished, sold again, etc. This blog will help you understand what an information product is, how to create it, and its types and benefits.
Information products are as many as information channels. Today’s information space offers many opportunities for streaming, blogging, and publishing. These three channels define the main products that can be created online. The table below shows the correlation between channels, info products, and tools used to make information products.
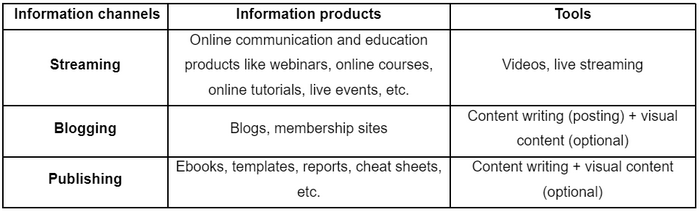
The table above can be expanded. More products and tools can be added, but the ones in the table are the most popular.
Information products have advantages that make them attractive to both customers and producers. Below are just some of the benefits you can get from buying or selling such products:
Information products have disadvantages, too. The value of information products depends on the value of the knowledge they contain, and you will never sell a single copy if your content doesn’t grab the readers’ attention. Still, the advantages above are essential factors that will help you understand how the information market works.

A short list of information products includes:
‘Ebook’ stands for ‘electronic book,’ which means a full digital copy of a regular book you can buy in a bookstore. An ebook is attractive because it can be downloaded in various formats suitable for all kinds of gadgets.
Another advantage is that it weighs nothing – in kilos, not kilobytes, of course. The physical weight is zero kilos and zero grams. This is especially relevant for people who like Charles Dickens or Leo Tolstoy.
Online courses and tutorials are a format that is becoming more and more popular. This is partly due to a shift in requirements for education. People no longer have time to get a new specialism at a college or university. Life has become more dynamic; now it is just six weeks or even less that we have to master a new skill or profession.
You can attend online courses and save the time that would be wasted in a college on studying disciplines you don’t need. Besides, you can attend digital courses any time you like.
Webinars are a variety of online courses but with greater interactivity opportunities. There is more communication, information exchange, and a practical focus here.
Live event recordings are a form of information product that might seem unimportant. However, they have a broad audience. Just think of thousands of fans who would pay for live streaming of their favorite concert or sports event.
Live event recordings are especially effective when they are an add-on to an existing product. For example, your product is a book, and the add-on is an interview with the actors from the screen version.
Live event recaps have a niche on the market as well. If a significant event occurs, concerned people might want a written copy. A bright example is Steve Jobs’ commencement speech. It was pronounced in June 2005 and is still quoted.
Membership sites are a special kind of information and communication tool. They are usually used to attract more customers to an existing product. For example, you can create online courses available to site members.
Q&As (questions and answers) are a format that can provide your users with important information on the usage of the existing product. It can be in the form of advice based on real-life experience.
The same refers to product cheat sheets, checklists, templates, and teardowns. These materials enhance the users’ understanding of your product or service. They make things transparent and, consequently, more attractive (as it is always rewarding to understand that you have a deep insight into the product you are working with). They will lead users through the whole process and explain things step by step, making the product easy to use.
Reports and analysis. These are, in fact, a summary of your hard work on some complex subject that you wish to share with the readers. It’s a description of your experience in a digest form. It is positioned as a shortcut for people who want an expert overview of the subject.

Let’s look at how to create information products on the example of an ebook. The steps below will help you understand what it takes to publish it.
The last step cannot be precisely measured in terms of time as your PR activities may cover an extended period (last as long as you are interested in selling your book) and have different intensity levels. You can make posts about your new or upcoming book every day or every month, creating the effect of suspense.
Information products are more competitive and more profitable than ‘tangible’ products. They can help you monetize your knowledge in a way that will require no expenses except those related to your creativity and writing skills.
We all think of saving a bit of time and are still wasting it on inefficient work. We have lots of valuable knowledge to share and still keep it to ourselves. Why not create a series of online lessons or write a teardown of your latest experience with the new software? This might bring you more money and publicity than the routine work you do every day.
Good luck with your technical writing!
ClickHelp Team
Author, host and deliver documentation across platforms and devices
Get monthly digest on technical writing, UX and web design, overviews of useful free resources and much more.
"*" indicates required fields