
What Is a Technical Report?
The definition of a technical report is the following: a technical report is a document written by a researcher; it describes how the research was conveyed: its phases, steps, results, peculiarities, etc., and may include deeper details like experimental data and outcome. It is a document that literally guides readers through the course of your work.
Who Needs a Technical Report?
Many organizations and companies use this type of technical documentation:
- Educational institutions
- Governmental organizations
- Commercial companies
- Non-profit organizations
As a rule, technical reports are widely used in the following industries: engineering, physical sciences, medical and biomedical fields, social sphere, etc.
Why Use a Technical Report?
If you have one of the following goals, a technical report will surely help you:
- You need to show the process of your work. Readers are interested in how you do it. Of course, results have a great value as well but how to check whether you’ve chosen the right way to get them?
- You need to represent important information. This type of technical documentation is often chosen to provide efficient communication among employees on different levels. For example, top management can make decisions based on the information given in technical reports. It means that a technical report may influence the way a company is going to develop in the future.
- You need to structure data. A technical report helps to represent information logically and show the cause-and-effect relations between the blocks of data.
- Attract the attention of readers to a problem. A technical report is a very good solution to show readers a problem and, of course, why it should be solved as soon as possible.
What Makes a Good Technical Report?
To write a high-quality technical report, you are to follow the rules that are common nearly for all types of technical documentation:
- Write for your readers: define your audience, their level of knowledge, organize the document the way they can easily use it;
- Use accurate, concise, and clear language;
- Eliminate errors: technical errors, inconsistencies, and errors in language;
- Use additional sources of information: references and visuals (diagrams, tables, graphs, etc.). For example, using diagrams can be very helpful if you need to show statistical data analyses. Our post – Using Diagrams in IT Documentation: Best Practices – will tell you more on how to use diagrams in technical documentation and which tools to choose;
- Keep your report short but informative.

What Is the Difference Between a Technical and Non-Technical Report?
Not every report can be called a technical one. Let’s figure out the difference between a technical report and a non-technical one.
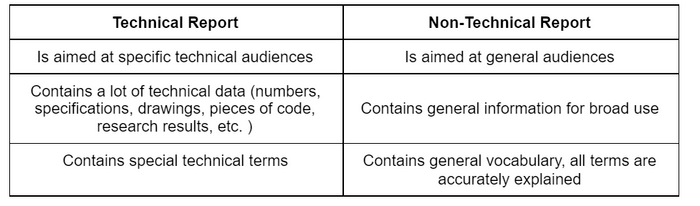
So, a technical report is a document that gives in-depth technical information. A non-technical report contains other types of information – more general ones. A popular report is a good example of a non-technical report. A popular report is a short document that describes the state’s or government’s financial performance.
Structure of a Technical Report
A technical report usually contains the following elements:
- Synopses. This is the first element of a technical report, but it should be the last thing to write. It is only a couple of paragraphs long. You are to underline your attitude to the problem, the methods used, the purpose, and the concept of the report.
- Title page. It is not only the title of the project, there should be some information about the author, their position, submission date, etc.
- Abstract. It is a short technical summary. As a rule, it is addressed to the audience. They decide whether to read the report or not, as they may already be acquainted with the problem.
- Table of contents (TOC). It is a guide to the report’s structure.
- List of illustrations. It is a list of diagrams, graphs, tables, or other materials that support the content of the report.
- Introduction. This is the introduction to the body of the report. Sometimes it contains relevant background information. This section describes the aims and objectives of the report, the scope of work, limitations, etc.
- Body. The longest and most important section of the report. It can be subdivided into logical parts. This is the main scope of work, ideas, methods, etc.
- Conclusion. Contains the answers to the questions that were specified at the beginning or solutions to the problems.
- Appendices. The list of references, books, etc.
- Glossary. The list of terms and symbols used in the report.
Formatting means highlighting some data or information. Formatting may include using corporate style guides to underline that the document belongs to a particular company, or it may include highlighting in order to underline the sense or importance of information. Sometimes, documents have both types of formatting.
Types of Technical Reports
Technical reports can be of various types depending on the industry, goals, and needs:
- Feasibility report. Is the most popular document at the beginning of the software development process. It helps teams make their choice between several options. It shows whether or not the task in question can be fulfilled with the specified resources.
- Business plan. It describes the goals of a business, methods of achievement, resources, timeline, etc.
- Technical specification. Describes requirements for a product or project and information on design and development.
- Research report. Is the result of an investigation: process and findings.
- Recommendation report. Contains recommendations to solve a problem.
- Policies and procedures. Contains guidelines for rational actions.
Even more types of technical reports can be singled out. The above-mentioned ones are considered to be basic.

Conclusion
If you are a newbie technical writer, now you surely know what a technical report is and how to write it; if you are an experienced one, you may find new ideas and sources of inspiration in this post. Whatever document you are creating, make sure you do your best to make it as clear as possible to your readers. Stay safe and create perfect technical documentation with ClickHelp!
Good luck with your technical writing!
ClickHelp Team
Author, host and deliver documentation across platforms and devices
 ClickHelp Teamin Technical Writing on 8/11/2021 — 4 minute read
ClickHelp Teamin Technical Writing on 8/11/2021 — 4 minute read ClickHelp Teamin Technical Writing on 8/11/2021 — 4 minute read
ClickHelp Teamin Technical Writing on 8/11/2021 — 4 minute read


