Artificial Intelligence (AI) stands at the forefront of technological innovation, promising to revolutionize the way companies operate. However, the path to integrating AI is fraught with challenges that can hinder its adoption.
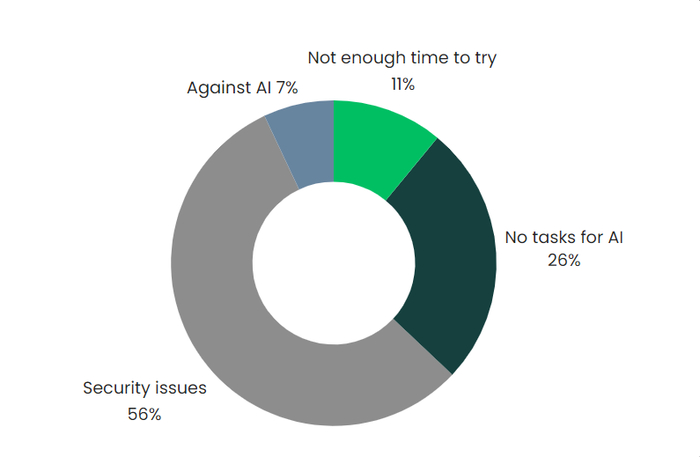
In a LinkedIn survey we conducted not long ago, we posed a simple question to our audience: “What reasons prevent you from using artificial intelligence (AI) when working with technical texts?” The results revealed that the majority cited security issues within their company, while others mentioned personal opposition to AI, uncertainty about applicable tasks, or a lack of time to explore AI solutions:
- The most significant barrier to using AI for working with technical texts is security concerns, with a majority of 56% citing this as a reason. This suggests that there is a substantial trust issue or a perceived risk associated with AI that needs to be addressed. Companies may worry about data breaches, misuse of sensitive information, or the AI acting unpredictably.
- The second most common reason, at 26%, is a lack of perceived need or relevance, indicating that a significant number of people do not see how AI can be applied to their work with technical texts. This could be due to a lack of awareness of AI’s capabilities or a belief that their tasks are too complex or unique for AI.
- A small percentage (7%) of respondents are opposed to AI on principle, which could stem from a variety of reasons, including skepticism about AI’s effectiveness, fear of job displacement, or ethical concerns.
- 11% feel they do not have enough time to try AI. This suggests that there may be a perception that integrating AI into their workflow is time-consuming or that the learning curve is too steep.
Overall, the results underscore the necessity for improved communication regarding the benefits and capabilities of AI, alongside the importance of addressing security concerns and enhancing accessibility and user-friendliness of AI tools to foster adoption.
In this blog post, we will examine the obstacles that businesses face when using AI, encompassing challenges ranging from data quality intricacies and privacy concerns to corporate culture’s resistance to change. Understanding these barriers is the initial stride towards unlocking AI’s transformative potential in the corporate realm.
What Prevents Technical Writers from Using AI in Daily Work?
Technical writers may encounter various obstacles when considering the integration of AI into their daily work. The most prominent reasons preventing writers from using AI are outlined below.
- Security concerns. As indicated by the survey results, over half of the respondents express hesitancy due to security issues within their company. This encompasses concerns regarding the protection of proprietary information, compliance with data privacy laws, and the risk of data breaches.
- Resistance to change. Some individuals may resist adopting AI due to discomfort with new technologies or a preference for traditional methods. They oppose AI, possibly out of fear of obsolescence or skepticism about its capabilities.
- Complexity of technical language. AI may struggle with the nuances of technical language, which can be highly specialized and context-dependent.
Addressing these challenges involves enhancing the security, usability, and accessibility of AI tools, as well as providing education and resources to help technical writers understand and leverage AI in their work.
Now, let’s focus on the three reasons listed above in more detail.
Security Concerns
When integrating Artificial Intelligence (AI) into the process of creating and managing technical documentation, several security concerns must be addressed to protect sensitive information and comply with data privacy laws. Here’s an overview of these concerns and potential solutions:
- Protection of proprietary information. Technical documentation often includes proprietary information such as trade secrets, confidential designs, or internal processes. AI systems that process this documentation could inadvertently expose such information if not properly secured.
- Compliance with Data Privacy Laws. Technical documentation may contain personal data subject to regulations like GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation) or HIPAA (Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act). AI systems must be capable of handling this data in compliance with such laws.
- Risk of data breaches. Like any digital system, AI systems are susceptible to cyber threats. A data breach could lead to the loss of sensitive technical information and personal data.
Dealing with Security Concerns
- Use AI engines with non-retentive memory. Choose AI engines that do not retain or utilize processed information for further machine learning, ensuring data confidentiality. Such AI engines are often referred to as ‘stateless’ or ‘non-retentive’ AI systems. These systems process data in real-time and do not store it for future use, ensuring information confidentiality. They anonymize input data, removing personal identifiers. Information is processed transiently, meaning it’s only used during the active session and not stored or logged. These systems often employ end-to-end encryption, ensuring data security during transmission and processing.
- Private accounts with data protection. Use private accounts that prohibit AI from using data for machine learning, adding an extra layer of security to prevent the AI from learning sensitive content. AnswerGenius in ClickHelp, for instance, now supports restricted documentation inclusion in its answers, making it configurable to show answers to everyone or only logged-in users. Private accounts, or more specifically, privacy-focused configurations in AI systems, can be designed to prohibit the use of data for machine learning purposes. These configurations typically ensure that data processed by the AI is isolated and not used for training or improving the AI model. The system does not retain data after processing, ensuring it cannot be used for future machine learning tasks.
- Regular updates and patches. Keep AI systems up-to-date with the latest security patches to protect against new vulnerabilities.
- Employee training. Educate employees on best practices for interacting with AI when handling technical documentation to prevent accidental leaks of sensitive information.
By addressing these concerns with careful planning and the right tools, organizations can leverage the power of AI in technical documentation while maintaining the security and privacy of their data.
Resistance to Change
Resistance to change is a common human response, especially when it comes to adopting new technologies like AI in the workplace. For example, many technical writers are comfortable with the tools and processes they currently use and may view new AI tools as unnecessary or disruptive to their established workflow. Besides, there may be concerns that AI could automate aspects of their job, leading to a fear of job loss or a reduction in the perceived value of their skills.
In addition, there are quality concerns. Technical writers often pride themselves on the accuracy and clarity of their work. They might be skeptical about an AI’s ability to match the nuanced understanding that a human brings to technical documentation.
Furthermore, writers may not trust AI to handle sensitive or complex information correctly, fearing errors or oversights that could have serious consequences.
Finally, people may often think about the time barrier. Indeed, the time and effort required to learn new AI tools and integrate them into daily tasks can be seen as a barrier, particularly if the benefits are not immediately clear.
Overcoming resistance to change involves addressing these concerns directly, demonstrating the value of AI as a complementary tool rather than a replacement, and providing adequate training and support during the transition period.
Complexity of Technical Language
The complexity of technical language can indeed pose a significant barrier to the adoption of AI by technical writers in their daily work.
Technical documents often contain specialized terms and jargon that are industry-specific. AI systems may not have been trained on such niche vocabularies, leading to misunderstandings or inaccuracies in the content they generate or edit.
Contextual nuance is an issue closely connected to the previous one. The meaning of technical terms can vary greatly depending on context. AI might struggle to discern these subtleties, which can result in content that is technically correct but contextually inappropriate.
These two problems become obvious when it comes to using AI for translation/localization purposes. To illustrate the problem, we have asked three AI-based tools (Google Translate, DeepL Translate, and ChatGPT 3.5) to translate the meaning of a technical term “Dutch folding” referring to sheet metal machining (a technique used to create a strong, folded edge on a metal sheet) into French, German, and Italian. The results are given in the table below:
| Google Translate | DeepL Translate | ChatGPT 3.5 | |
| French | pliage hollandais | pliage en néerlandais | pliage hollandais |
| German | holländisches Falten | niederländisch Falten | holländisches Falten |
| Italian | piega olandese | piegatura olandese | piega olandese |
The results in the table show that, despite the slight variations, all the three systems give a verbatim translation without taking into consideration the possibility of “Dutch folding” being a set phrase in English or referring to a limited field of usage (as a technical term). These results are useless from a localization perspective, as there are no corresponding concepts in any of the languages considered.
However, to be objective, it’s worth noting that ChatGPT provided its translation results with the following remark:
Please note that the context in which this term is used could affect the translation, especially in technical or industry-specific texts. It’s always a good idea to consider the specific context to ensure the translation is accurate.
To mitigate these issues, AI tools need to be carefully trained on domain-specific datasets and continuously updated to handle the evolving language of technical fields. Additionally, there should be a collaborative workflow where AI assists technical writers by automating routine tasks, allowing them to focus on more complex aspects of technical writing that require human expertise.

Conclusion
In summarizing the discussion on the obstacles of AI integration in businesses, it’s clear that companies must navigate through a labyrinth of ethical, technical, and cultural barriers to harness the full potential of AI. Yet, those who persevere will find themselves at the vanguard of innovation, reaping the benefits of increased efficiency, deeper insights, and a competitive edge.
Good luck with your technical writing!
ClickHelp Team
Author, host and deliver documentation across platforms and devices

